Topology
![]() Ethernet is a large, diverse family of frame-based computer networking technologies that operate at many speeds for local area networks (LANs) physical layers, the EtherCAT
Ethernet is a large, diverse family of frame-based computer networking technologies that operate at many speeds for local area networks (LANs) physical layers, the EtherCAT![]() ***EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs slave controllers close an open port automatically and return the Ethernet frame if no downstream device is detected. Slave devices can have several ports. Using these features, EtherCAT can support almost any physical topology, such as line, tree or star. The bus or line structure known from the fieldbuses
***EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs slave controllers close an open port automatically and return the Ethernet frame if no downstream device is detected. Slave devices can have several ports. Using these features, EtherCAT can support almost any physical topology, such as line, tree or star. The bus or line structure known from the fieldbuses![]() A Fieldbus is an industrial network system for real-time distributed control (e.g. CAN or Profibus). It is a way of connecting instruments in a plant design thus also becomes available for Ethernet.
A Fieldbus is an industrial network system for real-time distributed control (e.g. CAN or Profibus). It is a way of connecting instruments in a plant design thus also becomes available for Ethernet.
The combination of line and branches or stubs is also possible: any EtherCAT device with three or more ports can act as a junction, and no additional switches are required. The classic switch-based Ethernet star topology can be used either with switches configured to forward traffic directly between ports, or with special slave devices: the switches are then located between the network master and the slave devices.
The special slave device assembly (remember standard slave devices don't have a MAC address![]() A Media Access Control address (MAC address) is a quasi-unique identifier assigned to most network adapters or network interface cards (NICs) by the manufacturer for identification. If assigned by the manufacturer, a MAC address usually encodes the manufacturer's registered identification number) attached to one switch port together forms an EtherCAT segment, which is either addressed via its MAC address or via port-based VLANs. Since the 100BASE-TX Ethernet physical layer is used, the distance between any two nodes can be up to 100 m (300 ft). Up to 65535 devices can be connected per segment. If an EtherCAT network is wired in ring configuration (requiring two ports on the master device), it can provide cable redundancy.
A Media Access Control address (MAC address) is a quasi-unique identifier assigned to most network adapters or network interface cards (NICs) by the manufacturer for identification. If assigned by the manufacturer, a MAC address usually encodes the manufacturer's registered identification number) attached to one switch port together forms an EtherCAT segment, which is either addressed via its MAC address or via port-based VLANs. Since the 100BASE-TX Ethernet physical layer is used, the distance between any two nodes can be up to 100 m (300 ft). Up to 65535 devices can be connected per segment. If an EtherCAT network is wired in ring configuration (requiring two ports on the master device), it can provide cable redundancy.
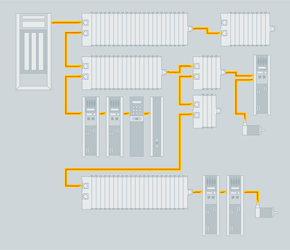
Figure 5-52: Flexible Topology: Line, Tree or Star
KAS controllers support line, tree, and star topologies. As the KAScontrollers (PCMM and AKD PDMM) have a singe EtherCAT port, ring topologies and cable redundancy is not supported.






